If you sell products you don’t manufacture yourself, finding reliable suppliers is one of the most crucial aspects of your business. While many companies turn to Chinese wholesale juggernaut Alibaba for inexpensive goods available in bulk, there are downsides to consider. Goods shipped from China can entail long delivery times, high shipping costs, and potential tariffs for the importer.
Product quality can also be an issue, as disreputable or fraudulent suppliers can make their way onto the platform. Finally, there may simply be more competitive prices elsewhere—if you know where to look. Read on to learn about popular alternatives to Alibaba.
What is Alibaba?
Alibaba is a business-to-business (B2B) online marketplace designed for merchants and retailers to purchase products in bulk, mostly from Chinese manufacturers and wholesalers. Ecommerce store owners can also use Alibaba to source and connect with suppliers who offer a dropshipping relationship.
The platform lets buyers research potential suppliers, negotiate prices, and collaborate with manufacturers to produce private-label products. By purchasing items in large quantities from Alibaba, merchants can potentially lower their product-sourcing costs. Buyers can also identify verified suppliers with a good reputation based on their past transactions on the platform.
8 Alibaba alternatives
- Shopify Collective
- IndiaMART
- Thomasnet
- tradeKorea
- Wholesale Central
- Trendsi
- DHgate
- Amazon Business
Here are a few of the largest and most reliable sites to consider if you’re looking for alternatives:
Shopify Collective
Shopify Collective connects US-based Shopify merchants with retailers who want to sell their products using the dropshipping model. All transactions take place within the Shopify ecosystem, so it’s easy to connect with reliable suppliers, add high-quality products to your online store, and make sales using Shopify Payments, a secure gateway that processes multiple payment methods like credit cards and digital wallets.
Shopify Collective accepts only suppliers who have an active Shopify store and accept Shopify Payments, which involves meeting Shopify Payments’ terms of service. Since only legitimate Shopify merchants can become suppliers on Shopify Collective, the platform has a higher standard for suppliers than Alibaba.
Pricing: Shopify Collective is a free tool for eligible Shopify merchants who submit an application to join the marketplace on the Shopify admin dashboard. You can create a Shopify account for $1 per month for the first three months.
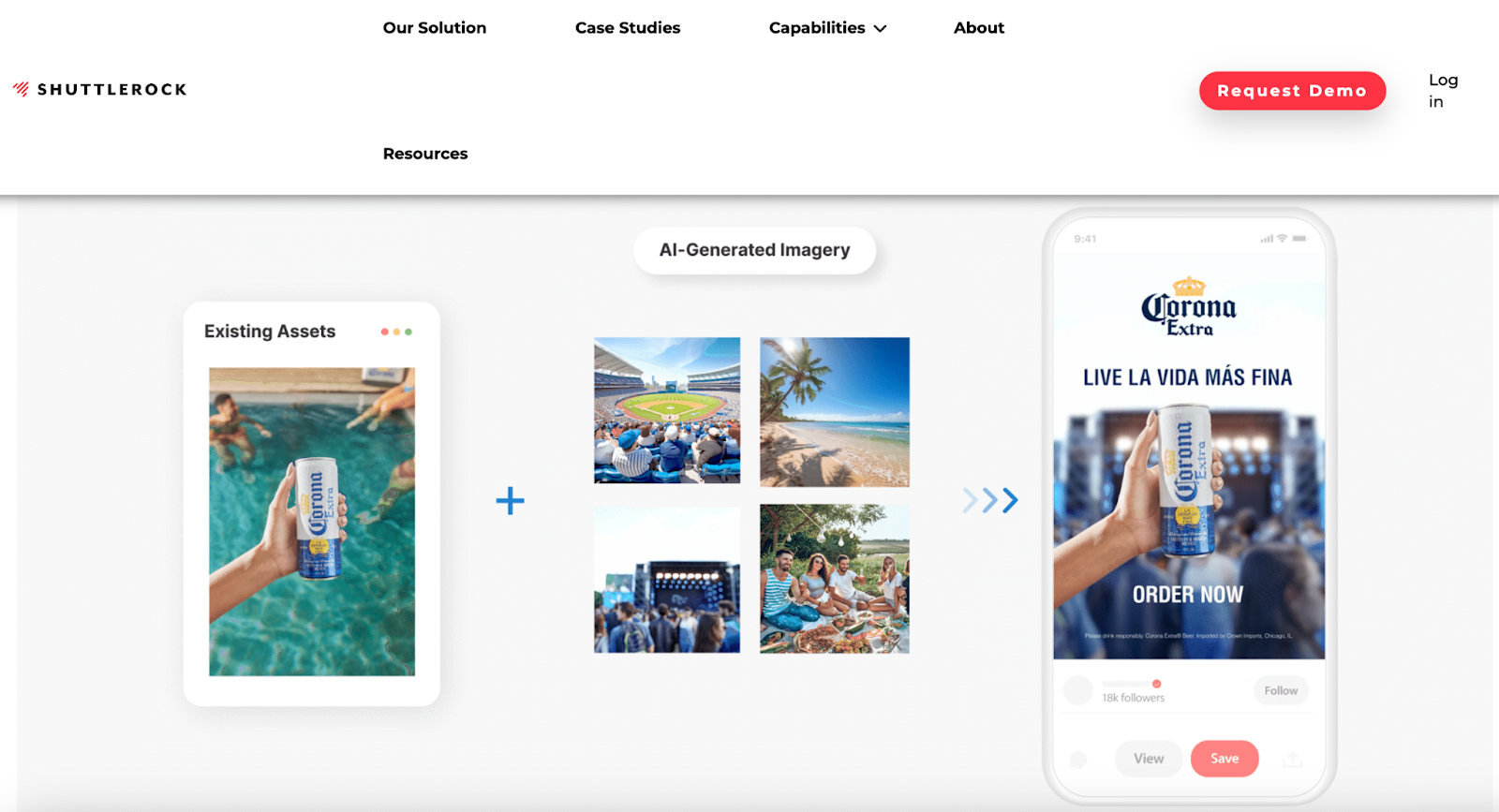
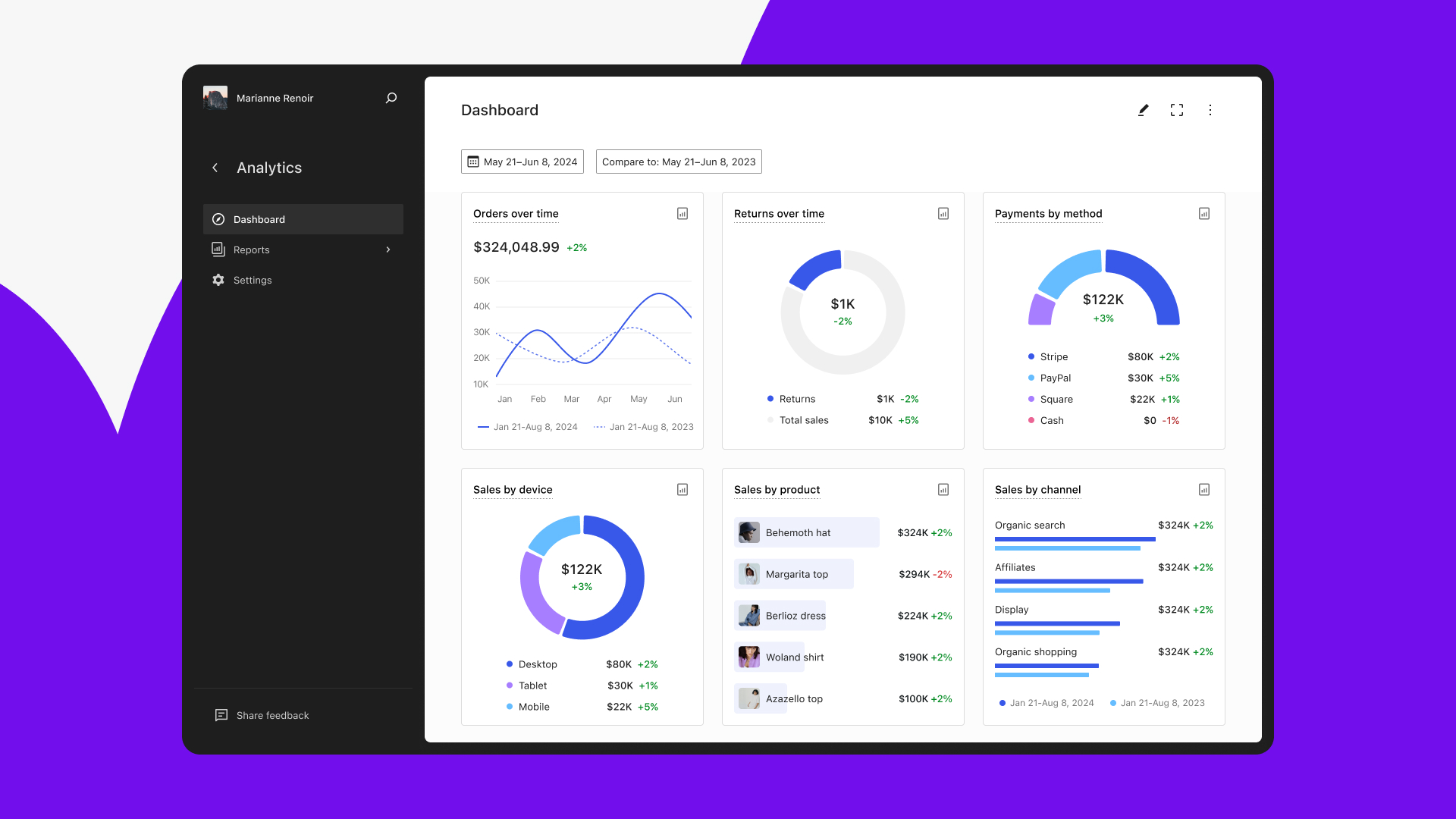
Find a product to sell
Connect with Shopify brands to sell their products. Use Collective to browse thousands of items, list them in your store, and ship them directly to customers.
Learn more
IndiaMART
IndiaMART is a B2B marketplace that sources products primarily from Indian suppliers. Some suppliers also offer dropshipping services. Dropshippers can search through a variety of product categories on the platform, from semi-finished materials like textiles to consumer goods like clothing and cookware.
Buyers on IndiaMART can use its Post Your Requirement feature with a detailed request (including order quantities and location preferences) and get a list of supplier recommendations from the platform.
IndiaMART’s suppliers are primarily in India, while Alibaba’s are mostly in China, which can impact trade costs and shipping time frames. IndiaMART is especially useful for buyers based in India, while Alibaba has more experience with international export orders.
Pricing: Buyers and sellers can sign up and use IndiaMART for free; sellers can sign up for premium subscriptions to boost lead generation, visibility, verification, and targeting.
Thomasnet
Thomasnet is an online marketplace that connects buyers and sellers of industrial equipment and supplies throughout the US and Canada. Merchants that manufacture their products can use Thomasnet to find production equipment and raw materials like plastic or metal. Thomasnet also includes a catalog of suppliers selling finished goods like office supplies, framed art, and boom microphones.
Although Thomasnet does not include a dropshipping feature like Alibaba, it can help merchants discover new suppliers to contact for a dropshipping arrangement. Thomasnet generally implements higher quality standards for suppliers than Alibaba and offers buyers a Supplier Discover tool that includes advanced search options like location filters, side-by-side supplier comparisons, and Supplier Profile Summary Reports that merchants can use to evaluate different suppliers and choose the right fit.
Thomasnet vets the basic business information of suppliers applying for Thomas Registered Suppliers Badges, and goes a step further for Thomas Verified suppliers by validating their entire product catalog, which helps items rank higher on search results. Sellers with Supplier Badges place higher on the platform’s search results and collections.
Pricing: Thomasnet is a free platform for buyers, but there is a 4.5% marketplace fee for suppliers without a Supplier Badge, which is accessible through a premium paid subscription. There are two Supplier Badge options: a Thomas Registered Supplier Badge for $100 per month and a Thomas Verified Supplier Badge for $250 per month.
tradeKorea
Sourcing items primarily from South Korean suppliers, tradeKorea is a wholesale marketplace with more than 100,000 manufacturers selling bulk inventory and raw materials. Some of the most popular product categories on the platform include consumer electronics, beauty and wellness products, kitchen goods, and even fertilizer material like groundnut meal and palm bunch ash.
The platform offers a few unique features, including a B2B matchmaking process where buyers can submit a form with procurement requirements and receive supplier recommendations based on that information. By leaning on the expertise of manufacturers in South Korea, tradeKorea generally offers higher-quality and more expensive products than Alibaba, especially in certain industries like technology and textiles.
Pricing: tradeKorea is a free online marketplace.
Wholesale Central
Wholesale Central is a US-based B2B directory that lists global suppliers selling products in bulk, including health, beauty, and wellness products, jewelry, electronics, and apparel. Wholesale Central includes a wide range of primarily North American dropshipping suppliers on its platform, helping dropshipping merchants find and interact with suppliers directly.
Although Wholesale Central doesn’t have an in-site messaging feature like Alibaba, it offers a more user-friendly search engine for finding niche items like organic wellness products or specialized supplements from a curated list of US-based dropshipping suppliers, including a specific directory for trending products. Wholesale Central uses a paywall and verifies suppliers on the platform, which helps buyers avoid the types of supplier scams on more open marketplaces like Alibaba. It also provides a calendar of upcoming supplier trade shows in North America where merchants can meet potential suppliers in person.
Pricing: Wholesale Central is free for buyers; suppliers pay a fee starting at $299 for a six-month listing. The platform doesn’t handle transactions or collect any related fees.
Trendsi
Founded in 2020 and based in California, Trendsi is a marketplace focused on connecting dropshippers and retailers with clothing suppliers. Ecommerce merchants can download and list dropshipping products directly through Trendsi’s free app. Trendsi works with reliable suppliers based in the US as well as trusted overseas vendors to source apparel and fashion accessories.
While Alibaba includes a huge selection of product categories, Trendsi focuses on high-quality apparel and fashion accessories sourced from North American suppliers. Buyers on Trendsi have the option to dropship individual items as well as purchase inventory in bulk for discounts.
Pricing: The Trendsi app is free for buyers but takes a percentage of every sale made on the platform and charges for shipping.
DHgate
DHgate is a wholesale marketplace that primarily sources products from Chinese manufacturers. Like Alibaba, DHgate uses customer reviews and a rating system to vet supplier quality, but it’s ultimately up to merchants to choose legitimate suppliers on the platform and avoid scammers. DHgate focuses on bulk orders and wholesale, but its suppliers generally offer a lower minimum order quantity (MOQ) than those on Alibaba, meaning buyers can purchase fewer items and still receive bulk discounts.
For example, suppliers on Alibaba often list MOQ requirements of around 500 or even 1,000 units, whereas DHgate suppliers often list an MOQ of around 100 or 50 (some even have no MOQ at all). DHgate’s product search engine includes a minimum order filter that you can use to find suppliers with MOQs that fit your company’s inventory needs. This means DHgate can sometimes be a better product sourcing option for small companies that have limited inventory requirements or want to test out a new product line before purchasing bulk inventory.
Pricing: DHgate is free to use, but the company takes a percentage of the sale amount on transactions made through the platform.
Amazon Business
Amazon Business is a B2B online marketplace designed for small and medium-sized businesses to purchase bulk inventory online from hundreds of thousands of suppliers across the globe. You can find a wide range of products on the platform, from office supplies to industrial equipment, consumer electronics, and beauty products. Merchants can purchase bulk inventory from Amazon Business or choose suppliers on the platform who provide dropshipping services and handle order fulfillment. According to a 2024 survey, the majority of products sold on Amazon are manufactured in China, with the United States being the second largest producer, and India coming in third.
Amazon Business’s selection of wholesale suppliers and products is more international compared to Alibaba, which almost exclusively features products from Chinese suppliers. Additionally, shipping is generally faster on Amazon Business than Alibaba, especially for Amazon Business Prime members who can choose from two-day, one-day, or even same-day shipping for certain products. By contrast, Alibaba’s international shipments using air or sea freight can take anywhere from five to 40 days.
Pricing: An Amazon Business account is free to use, but Amazon does charge referral fees using two methods: either a percentage of the total price or a minimum amount of 30¢. Amazon chooses whichever method is higher. Referral fee percentages range from 3% to 45%, depending on the product category.
An Amazon Business Prime Essentials account starts at $179 a year. Benefits include faster shipping, free shipping for select items, discounts on some bulk purchases, and better analytics tools, although referral fees still apply to Amazon Business Prime sellers.
Alibaba alternatives FAQ
Who is Alibaba’s biggest competitor?
Alibaba’s largest competitors in China include JD.com and DHgate, while large global competitors include companies like Amazon.
Is there a US equivalent to Alibaba?
Several US-based marketplaces offer services similar to Alibaba, including Shopify Collective, Amazon Business, Thomasnet, and Wholesale Central.
What should I look for in a supplier?
Choose a supplier with a good reputation for delivering high-quality products to customers within a reliable time frame. It’s also important to have a supplier that communicates clearly and promptly.
What is the best website to source from China?
There are several websites you can use to source products from China, including Alibaba, AliExpress, DHgate, JD.com, HKTDC, Made-in-China, and Taobao.